Unlike whisky which may be spelled whisky or whiskey in different parts of the world, gin is gin the world round. The name gin is derived from genièvre (French), jenever (Dutch), and ginepro (Italian), all of which mean “juniper”. It dates as far back at the 13th century.
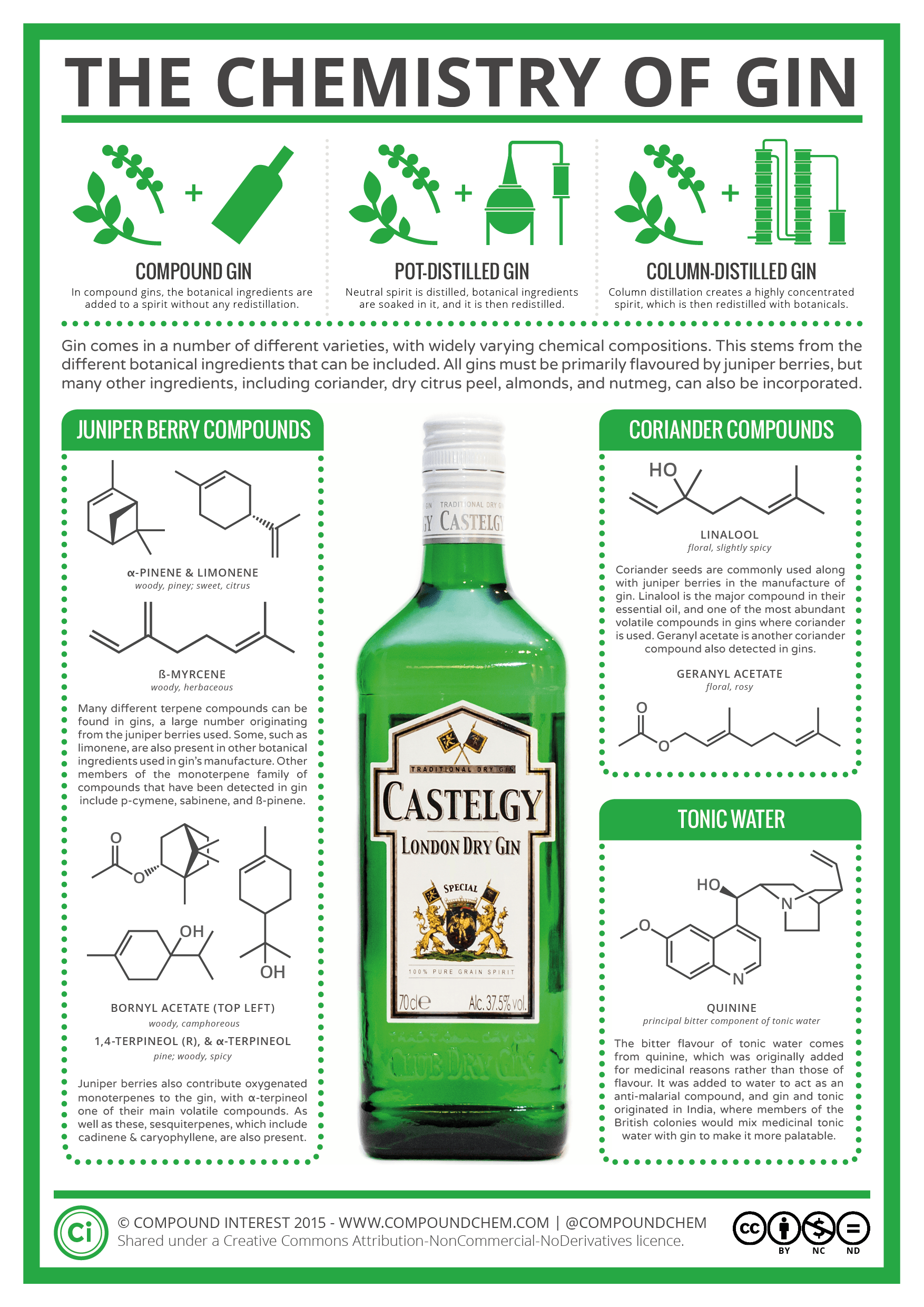
Before compounds from the botanical ingredients are extracted into the gin, the spirit is essentially flavorless. The flavor that’s imparted depends on the exact ingredients added, the specifics of which, for most gin makers, are a closely guarded secret. Gin is a spirit which derives its predominant flavor from juniper berries. Other ingredients that are used in some varieties of gin include anise, anglica, almonds, cinnamon, cassia root, and nutmeg, amongst many others.
Stay Informed: Sign up here for our Distillery Trail free email newsletter and be the first to get all the latest news, trends, job listings and events in your inbox.
Here’s the general class definition from the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau or TTB.
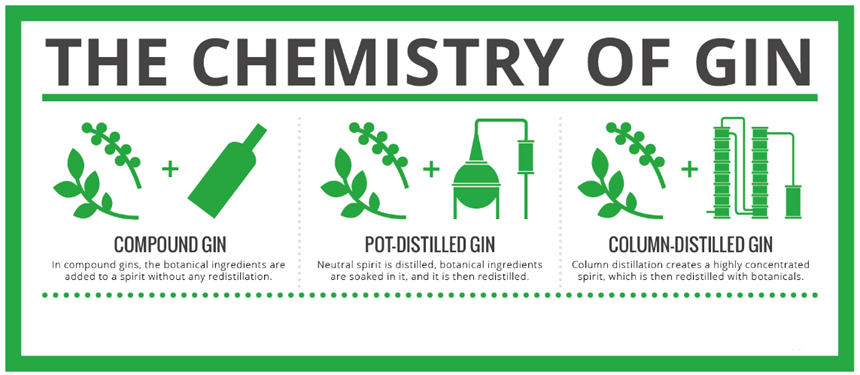
- Gin (Compounded) is juniper berries and (optionally) other aromatics or their extracts, essences or flavors blended with neutral spirits
- Gin (Distilled) is juniper berries and (optionally) other aromatics or their extracts, essences or flavors added to mash prior to distillation
- Gin (Redistilled) is juniper berries and (optionally) other aromatics or their extracts, essences or flavors added to distilled spirits prior to redistillation
- Gin Liqueur / Cordial – Wine, if used, may not exceed 2½% by volume of the finished product.
This handy infographic will make you wish you paid better attention in your chemistry class. As with other types of alcohol, there are a huge number of different chemical compounds present, but it’s possible to identify a range of significant chemical contributors to its aroma & flavor.
Click here to view the full size image.
EMBED THIS INFOGRAPHIC ON YOUR SITE
(Use this code to ensure proper source attribution.)